Contact Us
2025 How to Choose the Right Boiler Feed Tank for Your Needs
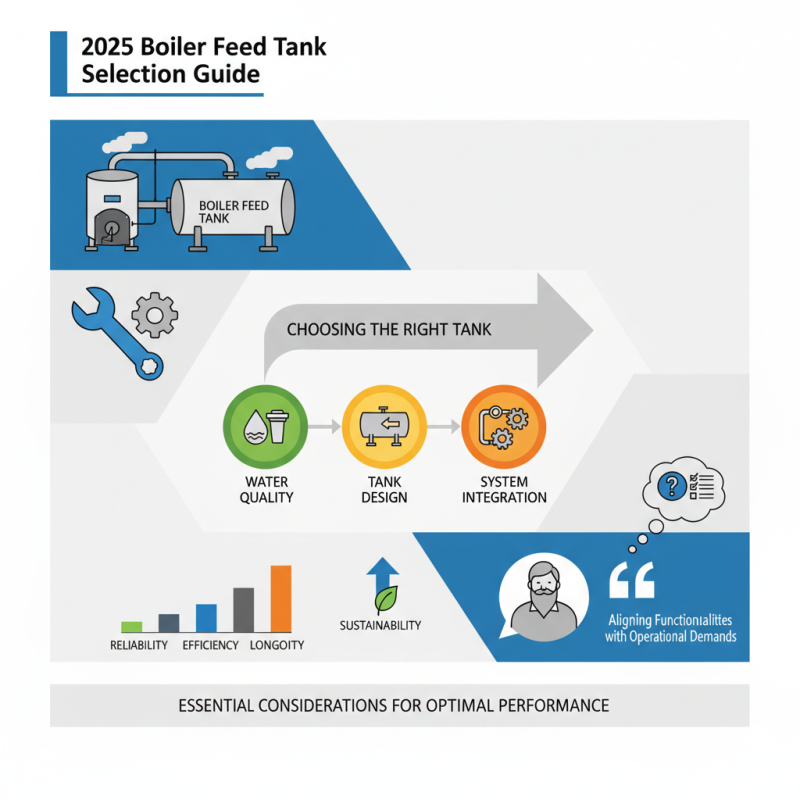
When choosing the right boiler feed tank for your specific needs, it's essential to understand the critical role these tanks play in ensuring the efficient operation of boiler systems. According to industry expert John Smith, a renowned engineer in thermal systems, "Selecting the appropriate boiler feed tank is not just a matter of capacity; it's about aligning your tank's functionalities with your operational demands." With a multitude of options available, ranging from varying capacities to diverse materials, getting the right fit can significantly affect your system's reliability and efficiency.
The right boiler feed tank will not only support your steam generation needs but also contribute to the overall performance and longevity of your boiler setup. Factors such as water quality, tank design, and integration with existing systems must be carefully considered. As the demand for energy efficiency and sustainable practices increases, the importance of selecting a suitable boiler feed tank becomes even more pronounced. In this guide, we will explore the essential considerations you need to keep in mind while navigating the selection process, ensuring that your choice effectively supports your operational goals.
Understanding the Purpose of Boiler Feed Tanks
Boiler feed tanks serve a crucial role in steam generation systems, primarily aimed at providing a steady supply of water to the boiler. Understanding their purpose is essential for ensuring optimal operation and efficiency.
These tanks operate by collecting condensate, which is recovered from the steam systems, and storing it until it can be fed back into the boiler. This not only maximizes water use but also reduces the need for additional water treatment processes, since the condensate is usually of high quality.
Additionally, boiler feed tanks help maintain system pressure and temperature, contributing to the overall stability of the boiler operation. They enable the removal of air and non-condensable gases from the water, which is vital for preventing corrosion and maintaining the longevity of the boiler system. By properly sizing and selecting a feed tank based on your specific requirements, you can optimize your steam production while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs. Understanding these functions will guide you in making informed decisions about your boiler feed tank selection, ensuring it meets the demands of your facility effectively.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Boiler Feed Tank
When selecting a boiler feed tank, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. One of the most crucial aspects is the capacity of the feed tank. According to industry reports, a tank's capacity should generally be sized to accommodate at least 1.5 to 2 times the maximum feedwater requirement of the boiler system. This buffer ensures the boiler can maintain consistent operation during peak demands, helping to prevent water starvation and possible damage to the system.
Another important factor is the material of the tank. Many industries have adopted stainless steel for its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in environments where feedwater could contain impurities. A study by the International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping highlights that using high-quality materials can extend the lifespan of boiler systems by up to 20%, significantly reducing maintenance costs. Furthermore, insulation is vital to maintain the temperature of the feedwater and minimize energy loss. Proper insulation can enhance the efficiency of the system, as noted in recent efficiency studies that indicate a potential 15% reduction in energy needs with appropriate thermal management.
Lastly, the design and configuration of the tank should be assessed according to the specific installation environment. Factors such as space constraints, location, and accessibility for maintenance should guide the choice of design—whether a vertical or horizontal configuration fits better. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) recommends thorough planning and adherence to safety standards in order to mitigate risks associated with operating high-pressure systems. By carefully considering these factors, users can select a boiler feed tank that not only meets their immediate needs but also supports long-term operational efficiency and safety.
Comparing Different Types of Boiler Feed Tanks Available
When selecting a boiler feed tank, it's essential to understand the different types available on the market. Typically, boiler feed tanks can be categorized into open and closed types. Open feed tanks are exposed to atmospheric pressure, allowing for easier maintenance and lower initial costs. However, they may require additional equipment for condensate return and may not be suitable for all applications. In contrast, closed feed tanks operate under pressure, providing enhanced efficiency and reduced risk of contamination, making them ideal for high-demand systems.
Tips: When considering a boiler feed tank, evaluate your specific application needs, such as the required pressure and capacity. Additionally, think about the maintenance demands of each type to ensure that it aligns with your operational capabilities. Incorporating energy-efficient designs can also save costs in the long run.
Another crucial aspect to consider is the material of the tank. Many boiler feed tanks are constructed from carbon steel, stainless steel, or polyethylene. Carbon steel tanks are robust and often more affordable, but they may be vulnerable to corrosion if not properly treated. Stainless steel tanks, while pricier, offer superior resistance to corrosion, making them a long-term investment for systems with high levels of moisture. Selecting the right material will greatly affect the lifespan and performance of your boiler feed tank.
Sizing Your Boiler Feed Tank for Optimal Performance
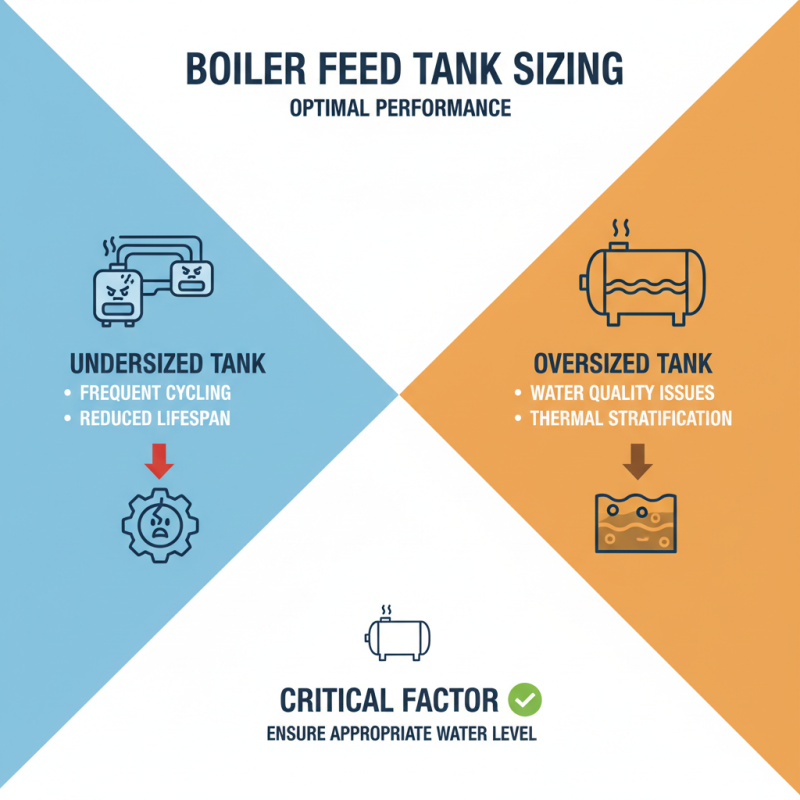
When selecting the right boiler feed tank, sizing is a critical factor to ensure optimal performance. The primary purpose of a boiler feed tank is to maintain the appropriate water level in the boiler, and its size directly influences the efficiency of the boiler system. An undersized tank may lead to frequent cycling, which can stress the system and reduce its lifespan, while an oversized tank can result in water quality issues due to stagnation and thermal stratification.
To achieve the correct size, several key parameters must be assessed, including the boiler’s capacity, the rate of steam production, and the water loss due to evaporation and blowdown. Additionally, considering peak and off-peak operating conditions is essential in determining the correct tank volume. Proper calculations, often based on the system's specific needs and operational patterns, will enable you to maintain a steady feedwater supply, reducing the risk of operational failures and enhancing efficiency. In conjunction with accurate sizing, integrating proper safety measures, such as level controls and alarms, ensures the boiler system operates smoothly and reliably.
Maintenance Considerations for Boiler Feed Tanks
When it comes to maintaining boiler feed tanks, regular inspections and preventative maintenance are crucial. Boiler feed tanks serve a vital role in ensuring a consistent water supply to the boiler system, which is essential for efficiency and safety. Therefore, addressing potential issues before they escalate can save both time and money. Implementing a robust maintenance schedule that includes checking for leaks, corrosion, and proper levels of water can enhance the lifespan of your boiler feed tank.
Tips: Regularly clean the tank to prevent the buildup of sludge, which can lead to inefficiency. Additionally, ensure that the water treatment program is adhered to; proper chemical dosing helps mitigate scaling and corrosion within the tank and connected piping systems.
Another important consideration is to monitor the tank's level controls and alarms. These components help maintain optimal water levels and prevent over-pumping, which can lead to operational disruptions. Conducting routine checks on these systems can help catch any discrepancies early and maintain smooth operation without unexpected downtime.
Tips: Invest in digital monitoring technologies that provide real-time data on the tank levels and chemical balances. This proactive approach can help streamline maintenance tasks and reduce the likelihood of costly repairs down the line.
2025 How to Choose the Right Boiler Feed Tank for Your Needs - Maintenance Considerations for Boiler Feed Tanks
| Criteria | Description | Maintenance Frequency | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tank Size | Determines the volume of water to be stored and feeds the boiler. | Annually | Ensure capacity matches boiler requirements. |
| Material | Material of the tank impacting durability and maintenance. | Biannually | Corrosion resistance is crucial for longevity. |
| Pump Type | Type of pump used to transfer water to the boiler. | Quarterly | Evaluate pump efficiency and functionality. |
| Level Control | System for monitoring and controlling water level. | Monthly | Regularly test for accuracy and response. |
| Safety Features | Includes pressure relief valves and emergency shut-offs. | Monthly | Ensure all safety mechanisms are operational. |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 10 Boiler Feed Tanks for Efficient Water Management
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Vertical Centrifugal Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of Boiler Feed Tanks in Maximizing Efficiency and Reducing Costs
-

Maximizing Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Liquid Propane Pump for Your Needs
-
2025 How to Choose the Right Propane Transfer Pump for Your Needs
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Boiler Condensate Pump for Your Home
