Contact Us
How to Choose the Right Liquid Propane Pump for Your Needs
Choosing the right liquid propane pump for your specific needs is crucial for ensuring efficiency and safety in handling propane. According to industry expert Martin Caldwell, a leading authority in liquid fuel systems, "Selecting the appropriate liquid propane pump can significantly streamline operations and enhance safety, making it a vital decision for both commercial and personal use." With an array of pumps available, understanding the specifications, application requirements, and safety features is essential for making an informed decision.
As propane use continues to expand in various industries, from residential heating to agricultural applications, the demand for reliable liquid propane pumps grows. Factors such as flow rate, pressure rating, and compatibility with different propane systems should guide your selection process. Ultimately, making the right choice will not only contribute to effective propane management but also ensure compliance with safety regulations, protecting both people and property.

Understanding the Different Types of Liquid Propane Pumps
When selecting a liquid propane pump, it's essential to understand the various types available, as each type is designed to meet specific needs and applications. The most common types include rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, and gear pumps. Rotary vane pumps are often favored for their efficiency and ability to handle high flow rates, making them suitable for commercial applications. These pumps utilize a rotating mechanism to create a vacuum and draw in the liquid propane, allowing for a smooth and continuous flow.
Diaphragm pumps, on the other hand, are known for their versatility and ability to handle various fluids, including propane. These pumps use a flexible diaphragm to create suction, providing a reliable pumping solution when handling corrosive or abrasive liquids. They are typically more compact and easier to maintain, making them ideal for residential uses or smaller operations. Gear pumps, driven by gears rotating in a chamber, are effective for precise flow rates and are often used in applications requiring consistent and steady output.
Ultimately, the choice of pump depends on factors such as the required flow rate, the specific application, and any limitations regarding space or maintenance. Understanding these different types of liquid propane pumps is crucial for selecting the right one for your particular needs, ensuring both efficiency and safety in your operations.
Liquid Propane Pump Types Comparison
This bar chart compares different types of liquid propane pumps based on their maximum flow rate (GPH). Understanding these specifications can help you choose the right pump for your specific needs.
Assessing Pump Capacity and Flow Rate Requirements
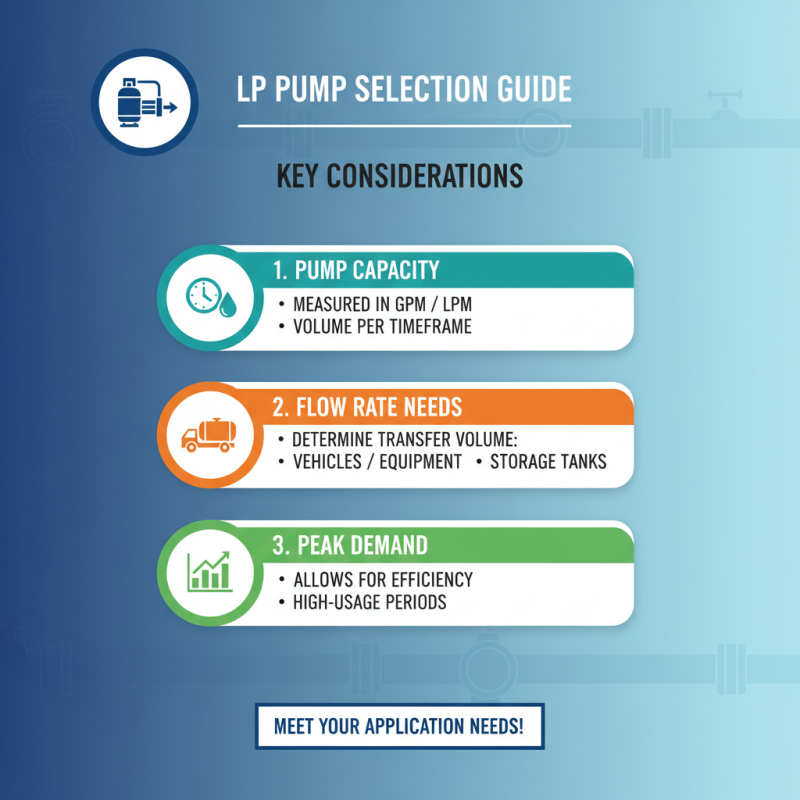
When selecting a liquid propane pump, understanding pump capacity and flow rate requirements is crucial to meet your specific application needs. The pump capacity is typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM) and indicates how much liquid propane can be moved within a certain timeframe. Assessing your requirements starts with determining the volume of propane you need to transfer, which can vary widely depending on whether you’re fueling a vehicle, powering equipment, or refilling storage tanks. It’s important to consider peak demands, allowing for some additional capacity to ensure efficiency during high-usage periods.
Flow rate is just as vital, as it affects how quickly your tasks can be completed. If your operations require rapid fuel delivery, a pump with a higher flow rate is essential. Conversely, if a slower delivery suffices, a lower flow rate pump can be more economical. Additionally, you should consider the viscosity of the liquid propane and any potential pressure losses due to lengthy hoses or connections. Evaluating both the pump capacity and flow rate in relation to your specific usage will help you choose the right liquid propane pump for optimal performance and reliability in your operations.
Evaluating Material Compatibility and Durability
When selecting a liquid propane pump, evaluating material compatibility and durability is critical to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Various materials exhibit different resistance levels to the corrosive properties of liquid propane. According to a 2022 industry report, stainless steel remains a preferred choice due to its robustness and resistance to corrosion, particularly in environments with high humidity or exposure to the elements. For instance, pumps made from 316 stainless steel are noted for their superior performance in handling liquid propane, making them less susceptible to wear over time compared to traditional materials.
In addition to material selection, durability is paramount when assessing propane pumps. A study conducted by the Pump Manufacturers Association highlighted that the average lifespan of a pump significantly correlates with its materials; those constructed with reinforced polymer composites displayed enhanced durability under high-pressure conditions, without compromising on weight efficiency. Furthermore, the incorporation of high-quality seals and valves can prevent leakages and maintenance issues, reducing operational downtime. Evaluating these factors can result in significant cost savings and increased reliability for any operation requiring liquid propane transfer.
How to Choose the Right Liquid Propane Pump for Your Needs
| Feature | Description | Material Compatibility | Durability Rating | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pump Type A | High flow rate with minimal pressure drop. | Compatible with standard LP gas. | 4.5/5 | Residential heating and commercial use. |
| Pump Type B | Compact design for limited space. | Suitable for propane, not for corrosive liquids. | 4.0/5 | Portable applications and heating solutions. |
| Pump Type C | Heavy-duty model for high demand. | Compatible with LPG and certain industrial chemicals. | 5.0/5 | Industrial applications, agriculture, and fuel transfer. |
| Pump Type D | Self-priming functionality for ease of use. | Only compatible with liquid propane. | 4.8/5 | Home heating systems, outdoor grills. |
Considering Power Source Options for the Pump
When selecting a liquid propane pump, one of the most critical factors to consider is the power source that will drive the pump. The choice between electric, gas, and battery-powered pumps can greatly influence both efficiency and convenience. Electric pumps are often favored for their ease of use and quiet operation, making them suitable for residential or light commercial settings. They can be plugged into standard outlets, which makes installation straightforward, but checking the electrical load requirements is essential to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
On the other hand, gas-powered pumps offer mobility and high-power output, making them ideal for outdoor or remote applications where electricity is not readily available. These pumps typically provide greater suction capability and can handle larger volumes of propane, but they require careful consideration regarding fuel type and availability during operation.
Battery-powered options present another viable alternative, especially for small-scale operations or scenarios where portability is essential. These pumps are typically lightweight and can be used in locations without access to traditional power sources, but users should evaluate battery life to avoid disruptions during extended use.
Key Features and Safety Standards to Look For
When selecting a liquid propane pump, understanding the key features and safety standards is crucial for ensuring efficiency and safety. One essential feature to consider is the pump’s flow rate, often measured in gallons per minute (GPM). A pump with a higher flow rate can significantly reduce filling times; however, it’s important to match this with your specific needs. Industry reports indicate that pumps with a flow rate between 5 to 20 GPM are commonly used for home heating and recreational applications, providing a balance between performance and handling capacity.
Safety standards also play a pivotal role in selecting a propane pump. Look for units that comply with OSHA regulations and are recognized by the ANSI or NFPA standards. These standards ensure that the pump is designed to mitigate risks associated with flammable liquids, including leak prevention and proper ventilation. Additionally, features such as automatic shut-off valves and emergency stop buttons enhance user safety during operation. Regularly consulting updated safety guidelines and standards, such as those published by the Propane Education & Research Council, can provide invaluable insights into the best practices.
Tips: Always read the manufacturer's safety instructions carefully before use and ensure that your pump is equipped with necessary safety features before installation. Keeping your pump well-maintained is also vital; regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they become safety hazards.
Related Posts
-

Maximizing Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Liquid Propane Pump for Your Needs
-

Maximizing Efficiency: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Vertical Centrifugal Pump for Your Needs
-

Why Canned Pumps Are Essential for Efficient Fluid Transfer in Industries
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Boiler Condensate Pump for Your Home
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Right Vertical Turbine Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of Boiler Feed Tanks in Maximizing Efficiency and Reducing Costs
