Contact Us
2025 How to Choose the Right Propane Transfer Pump for Your Needs
When it comes to selecting the ideal propane transfer pump for your specific needs, expert advice can significantly streamline the decision-making process. John Smith, a renowned specialist in the propane industry, emphasizes that "the right propane transfer pump can enhance efficiency, reduce risks, and ultimately save you both time and money." With various pumps available on the market, understanding the distinct features and capabilities is essential for making an informed choice.
In the ever-evolving landscape of fuel handling, the importance of choosing a suitable propane transfer pump cannot be understated. Factors such as flow rate, portability, and safety features all play a critical role in ensuring that the pump meets both operational needs and safety regulations. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore key considerations for selecting a propane transfer pump, equipping you with the knowledge to identify the best option for your applications. Whether you're in agriculture, construction, or industrial operations, the right pump can make all the difference in efficient fuel transfer, keeping your projects on track and maintaining productivity.
Understanding Propane Transfer Pumps: Key Functions and Uses
Propane transfer pumps play a crucial role in various applications, from residential heating to commercial usage. Understanding their key functions can help users make informed decisions when selecting a pump that meets their needs. Primarily, these pumps are designed to move propane efficiently from one location to another, whether it's from a storage tank to a vehicle or from a larger tank to smaller containers. This process is facilitated by an array of features including safety mechanisms, flow rates, and the type of power source, which can vary widely based on application and user requirements.
In addition to their fundamental function of transferring propane, these pumps can also be equipped with various accessories that enhance their usability. For example, some models include automatic shutoff features, which prevent spills and improve safety during the transfer process. Additionally, the size and design of the pump can affect how easily it can be operated in different environments, whether for outdoor construction sites or indoor applications. Understanding these functionalities and the specific needs of your operation can help ensure that you choose the right propane transfer pump, ultimately enhancing efficiency and safety in handling propane.
Identifying Your Needs: Assessing Requirements for a Propane Pump
When selecting a propane transfer pump, the first step is to identify your specific needs, considering factors such as the volume of propane you intend to handle, the frequency of use, and the distance the fuel must be moved. For instance, if you are a homeowner who only occasionally requires propane for grilling or heating, a portable, lower capacity pump may suffice. In contrast, businesses with regular high-volume needs—like those in agriculture or commercial heating—may require a more robust system capable of transferring larger quantities efficiently.
Next, assess the environment in which the pump will be used. Factors such as the location (indoors or outdoors), accessibility to power sources, and climate conditions can significantly influence your decision. For outdoor use, a pump designed to withstand varying weather conditions may be necessary. Additionally, consider safety features, such as automatic shut-off valves and vapor recovery systems, to ensure safe operation. Thorough evaluation of these requirements will guide you in choosing a propane transfer pump that not only meets your operational needs but also operates safely and efficiently.
Types of Propane Transfer Pumps: Selecting the Right One for Your Application
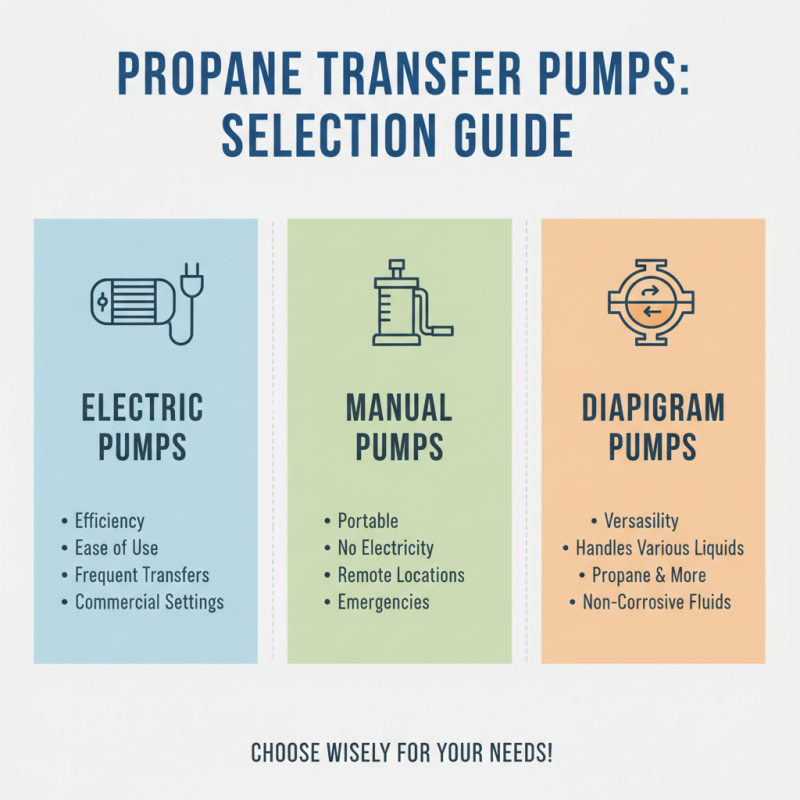
When selecting the right propane transfer pump for your specific application, it’s essential to understand the different types available and their suitability for your needs. The most common types include electric, manual, and diaphragm pumps. Electric pumps are favored for their efficiency and ease of use, making them ideal for frequent transfers in commercial settings. Manual pumps, on the other hand, are portable and do not require electricity, which makes them beneficial for remote locations or emergencies. Diaphragm pumps offer versatility and can handle a variety of liquids, providing options for both propane and other non-corrosive fluids.
In addition to considering the type of pump, it’s important to evaluate the flow rate and pressure requirements for your application. Higher flow rates typically facilitate faster transfers, essential for large-scale operations, while lower flow rates might be sufficient for smaller tasks. Additionally, check the pump's compatibility with your propane storage system, ensuring that fittings and connections align properly. Understanding your operational needs, frequency of use, and environmental conditions will ultimately guide you in selecting the most suitable propane transfer pump for your requirements.
Important Features to Consider When Choosing a Propane Transfer Pump
When selecting a propane transfer pump, it’s essential to consider several critical features that directly impact its efficiency and safety. According to recent industry reports from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), propane transfer operations can increase risks if the equipment used is not compliant with safety standards. A good propane transfer pump should have a durable construction, often made from materials resistant to corrosion and wear, ensuring longevity even in demanding environments. Additionally, a pump with a clear flow rate specification is vital; pumps typically range from 10 to 30 gallons per minute, and choosing the right flow rate can optimize your operations while minimizing risks associated with overfilling or spills.
Another significant feature to consider is the power source of the pump. Electric pumps are efficient and generally require less maintenance, whereas gas-powered models are portable and can be used in areas without electrical access. As highlighted by the Propane Education & Research Council (PERC), understanding your operational context is essential in making the right choice. Noise levels and ease of mobility should also not be overlooked. Many users prefer pumps that have built-in noise reduction technology and ergonomic designs for easier handling and transport. The right combination of these features will ensure a safe and seamless propane transfer experience, tailored to meet your specific operational needs.
2025 Propane Transfer Pump Features Comparison
This chart illustrates the important features to consider when choosing a propane transfer pump. The data highlights typical values for various features such as flow rate, maximum lift, power source, tank size, and weight that are relevant in evaluating different pumps.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices for Using Propane Transfer Pumps
When using propane transfer pumps, safety should always be the top priority. First and foremost, it's essential to ensure that the workspace is well-ventilated to prevent any accumulation of propane vapors, which can pose a significant hazard. Proper personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn to safeguard against any accidental splashes or leaks. Before operating the pump, users should conduct thorough inspections for any signs of damage or wear in both the pump and the hoses to ensure safe operation.
Additionally, understanding the proper handling techniques is crucial for maintaining safety. Always ensure that the transfer area is clear of any ignition sources, as propane is highly flammable. It's advisable to have a fire extinguisher readily available and to be familiar with emergency protocols in case of a leak or fire. During the transfer process, users should never leave the pump unattended and should monitor the flow closely to prevent overfilling or spills. By adhering to these best practices, users can significantly reduce the risk associated with propane transfer operations.
Related Posts
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Right Vertical Turbine Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of Boiler Feed Tanks in Maximizing Efficiency and Reducing Costs
-

2025 Top 10 Boiler Feed Tanks for Efficient Water Management
-

Why Canned Pumps Are Essential for Efficient Fluid Transfer in Industries
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Pressure Pumps for Your Needs
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Boiler Condensate Pump for Your Home
